Also in the area of E-commerce internationalization is a current topic, on the one hand to reach consumers in other markets and on the other hand to generate brand loyalty. If you want the best possible SEO traffic optimization for your website in other languages and other countries, you need to make a few decisions in advance and also meet a few requirements. These make it possible to achieve profitable synergy effects between the individual country pages through the right internationalization strategy.
Top-level domain, subdomain or subfolder?
If you have decided to have your online offering appear in other languages and other countries, you should first decide how you want to present the new, foreign-language Content would like to host. Basically, there are advantages and disadvantages to each variant from an SEO perspective.
Subdirectories for all languages used:
The advantage of this variant is that the costs for website hosting - as only one domain is used - are kept within reasonable limits. In addition, the root domain benefits from the incoming links from external sites. However, this variant is disadvantageous in terms of geotargeting, as the Backlinks aus den unterschiedlichen Ländern kumulieren ebenfalls auf einer Root-Domain. Das Resultat sind nicht eindeutige Linksignale für Google, woraus Targeting-Probleme des richtigen Ländersubfolders resultieren können. Zudem eignen sich länderspezifische Top-Level-Domains, die mit einer länderspezifischen Domainendung einhergehen nicht für diese Variante, denn für ausländische Besucher wirken sie abschreckend, was letztlich zu niedrigeren Klickraten führt.
Example:
- www.companyurl.com/de
- www.companyurl.com/fr
- www.companyurl.com/es
Subdomains for all languages used:
With this variant, hosting fees are also only charged for the root domain, as any number of subdomains can be installed on it. However, subdomains behave like independent domains, so that the power of external links is not forwarded one hundred percent to the root domain. Accordingly, the links between the subdomains behave like external links, so that there is a need for country-specific link marketing.
Example:
- en.companyurl.com/
- fr.companyurl.com/
- es.companyurl.com/
Country-specific top-level domains:
This variant is the most administratively complex, but makes the most sense from an SEO perspective, as it provides the opportunity for targeted country-specific link marketing. Due to the fact that all domains work independently of each other, the Search results is more credible for the user - because they are redirected to a country-specific top-level domain. Although this variant is generally associated with more effort and higher costs, it pays off in the long term from an SEO perspective. It also makes sense to use parameter-based language control and Javascript as both are sometimes unreadable for Google or cause confusion. However, contrary to previous assumptions, it is now known that it is not necessary to host the respective language version of the website on a server in the corresponding target country.
Example:
- www.companyurl.de/
- www.companyurl.com/
- www.companyurl.es/
Different language versions in one country
If you want to operate a website with different languages in a particular country, you should opt for a hybrid of the three variants presented above. For example, if a Swiss company wants to generate its website in both German and French, a mixture of a top-level domain and a subdomain is possible. In addition, the GoogleWebmaster-tools for top-level domains such as xyz.com, xyz.net or xyz.org, which Subdomain or which subfolder is assigned to which language. The use of a meta tag in the Source code the website, the desired target language must be transmitted to the search engines. The so-called meta tag "language" works syntactically and in relation to the example above as follows:
Example:
- en.companyurl.ch
- fr.companyurl.ch
How to link country pages effectively: "hreflang" - TagTitel
Nevertheless, despite the application of the measures explained, it can happen that German websites rank ahead of the specific country versions in Austria or Switzerland, for example, because they have a greater Relevance for Google and stronger SEO signals. As a result, Austrian customers of an online store, for example, see the wrong currency, delivery area or inappropriate user approach. Google was also aware of this fact and introduced the hreflang-attribute has provided a remedy. This attribute allows the different language versions to be transmitted directly to Google so that the specific country versions of the associated target country are strengthened. For example, if you operate an online store in Austria and have a Country domain for Germany can check the presence of its language version in the head section of its Austrian website with the hreflang-attribute for Germany clearly communicate to Google:
Example:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="ch" href="https://www.companyurl.ch/" >
This option can also be used in a multilingual country such as Switzerland to tell Google exactly which language region the respective page is intended for:
Example:
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="de-CH" href="https://de.companyurl.ch/" />
<link rel="alternate" hreflang="fr-CH" href="https://fr.companyurl.ch/" />
It is also advantageous that the introduction of the hreflang tag means that the Content of a German-language German, Austrian or Swiss domain does not necessarily have to be unique in order to prevent a devaluation by Google. Rather, Google recognizes that the different websites are intended for different markets, whereby the Duplicate Content is justified. However, this code must be implemented on every subpage that has an identical page on another domain.
Other countries, other customs - the content of the websites
However, it is not only the aforementioned technical adaptations that are decisive for the creation of websites, but also their content. The content of the different language versions should not only be coherent, but should also match the technical signals of the respective page for Google. Accordingly, it makes sense for all texts that have titles and meta descriptions and the URLs to be written in the respective language of the corresponding domain. This is the only way to ensure that unambiguous signals are communicated to Google. Furthermore, the Keyword-The search engine can be adapted to the specific search behavior of the country in question. It happens that the same product or Keyword in a country a very high Search volume and, on the other hand, has very little in another country. Relevance owns. There are many reasons for this fact, which means that, in addition to cultural and climatic factors, it also depends on the population of the country in question:
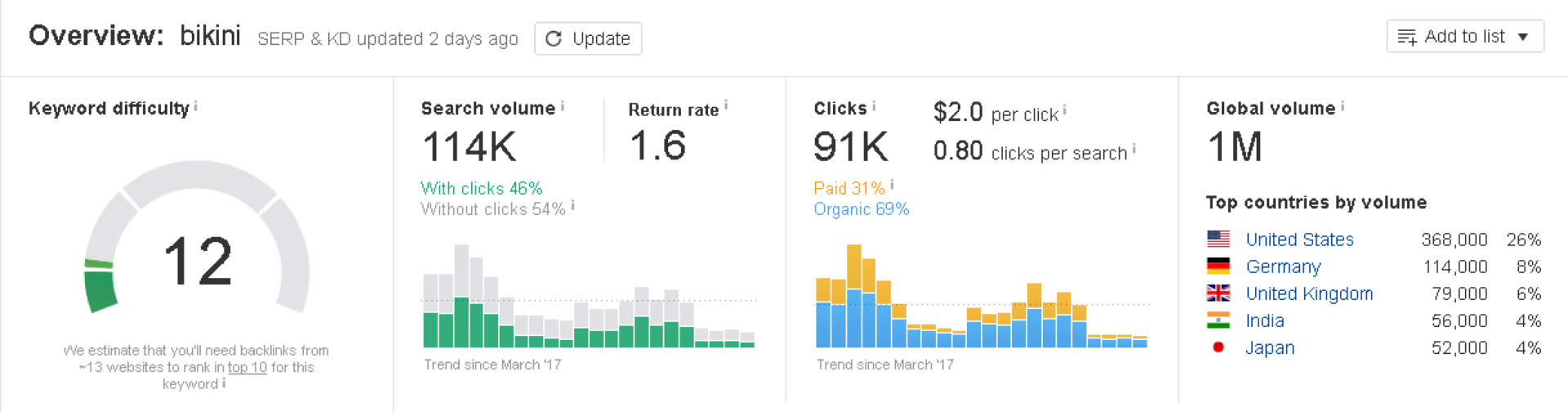
- Monthly Search volume Search word: "Bikini" in Germany (Google DE): 114,000
- Search volume per month for the search term "bikini" in Italy (Google IT): 33,000
- Monthly Search volume Search term "bikini" in Norway (Google NO): 14,000
Differences also arise when a language is spoken in different countries or regions, such as German in Germany, Switzerland and Austria or French in France, Canada and Switzerland. The different cultural influences not only lead to a different use of words, but sometimes also to different meanings. In Switzerland, for example, the word "Velo" is generally used for the term "bicycle". It therefore makes sense that Keyword-targeting should also be designed differently for the various country domains, as this is the only way to take account of regional differences.
Summary:
Basically, it can be said that certain technical requirements must be met for a successful internationalization strategy on the one hand, and that the content of the websites or the specific country domains must be tailored to the respective target country on the other. Unlike the technical set-up, which requires a great deal of work, especially at the beginning, which decreases over time, the creation of content is a continuous process. This should - right from the start - be tailored to the cultural characteristics and needs of the users in the respective target country. It therefore makes sense to take a closer look at the characteristics of the target country and consider working with native speakers.